Breaking Update: Here’s a clear explanation of the latest developments related to Breaking News:The Real Reason Washington Wants Venezuela’s Oil– What Just Happened and why it matters right now.
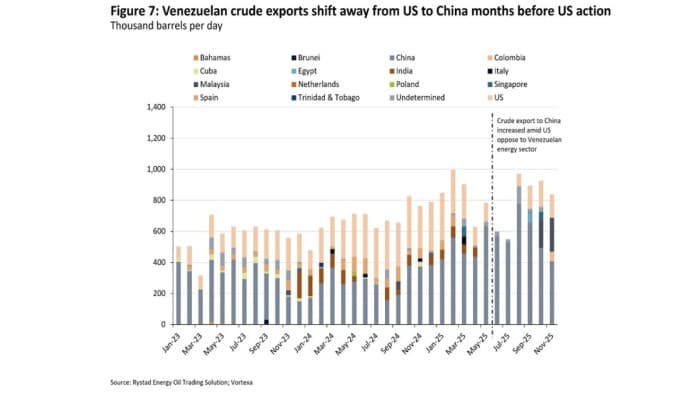
The timeline of the US–Venezuela conflict highlights a long-term strategy centered on securing heavy crude supplies for US Gulf Coast refineries, which are configured to process heavy sour barrels and benefit from Venezuela’s ability to deliver crude over short lead times. This will reduce reliance on Middle Eastern high-sulfur fuel oil (HSFO) for the US. Exports of Venezuela crude are expected to recover slowly toward the US, Europe and India, leaving China disadvantaged, while OPEC+ remains defensive.
US Gulf Coast refineries process nearly 1.45 million bpd of imported crude out of an average 9 million bpd in total refinery runs. With between 400,000 and 500,000 bpd of Venezuelan crude (primarily Merey) expected to be added, nearly 5% of West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude intake could be replaced by Venezuelan Merey. We used linear programing (LP) modeling (AVEVA) for some Gulf Coast refineries (having coker, catalytic cracker and hydrocracker) to estimate changes in product yields and utilization rates of heavier oil-processing units. The results indicate an average 2% increase in diesel yield, primarily higher utilization of bottom of barrel units, driven by increased utilization of heavy conversion units by almost 2% to 3%.
Over the longer term, as Venezuelan crude production just exceeded 900,000 bpd in 2025, with anticipated US capital inflow and a subsequent demand increase, Rystad Energy expects the Venezuelan refining sector – which has 1.2 million bpd of capacity – to start increasing runs within 18 to 24 months. Current run rates are hampered by frequent power disruptions, unplanned outages and improper maintenance of the refineries. We assess that the typical turn-down rate of 60% should be feasible by the middle of next year.
China remains the primary loser in this evolving structure. The loss of heavily discounted Venezuelan crude undermines the economics of independent so-called ‘teapot’ refiners and places approximately $12 billion in oil-backed loans at risk. Although some Middle Eastern HSFO and heavy barrels may now be redirected toward Asia, Chinese refiners still face higher feedstock costs, longer shipping distances and elevated geopolitical risk compared with the Venezuelan barrels they previously imported. India, by contrast, stands out as a structural winner, with complex refineries well suited to heavy sour grades and a renewed opportunity to absorb Venezuelan crude as sanctions ease.
Venezuelan crude accounts for approximately 500,000 bpd of the 15 million bpd in China refinery runs since around 2019, which marked the start of increased US opposition to the Venezuelan energy sector. Chinese refineries processing heavy crudes are typically integrated facilities equipped with heavy bottom-of-the-barrel upgrading units. As a result, the loss of heavy Venezuelan barrels is unlikely to have any noticeable impact on China’s overall product yields, given total refinery runs of around 15 million bpd. While individual refiners processing this crude will need to adjust their crude slate, these changes are not expected to affect aggregate Chinese yields materially.
Disclaimer: The opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author, and do not necessarily represent the views or beliefs of Rystad Energy.
By Pankaj Srivastava for Rystad Energy
More Top Reads From Oilprice.com